Catalyst & Chemicals
Tailor-made catalysts for optimum productivity in your process.
Hindustan Platinum is a leading manufacturer of precious metal catalysts that play a pivotal role in chemical industries, owing to their activity, selectivity and recyclability. Our catalysts are abundantly supplied to API and its intermediaries, Agrochemicals, Flavours & Fragrances and Fine & Bulk Chemical industries.

Industries We serve
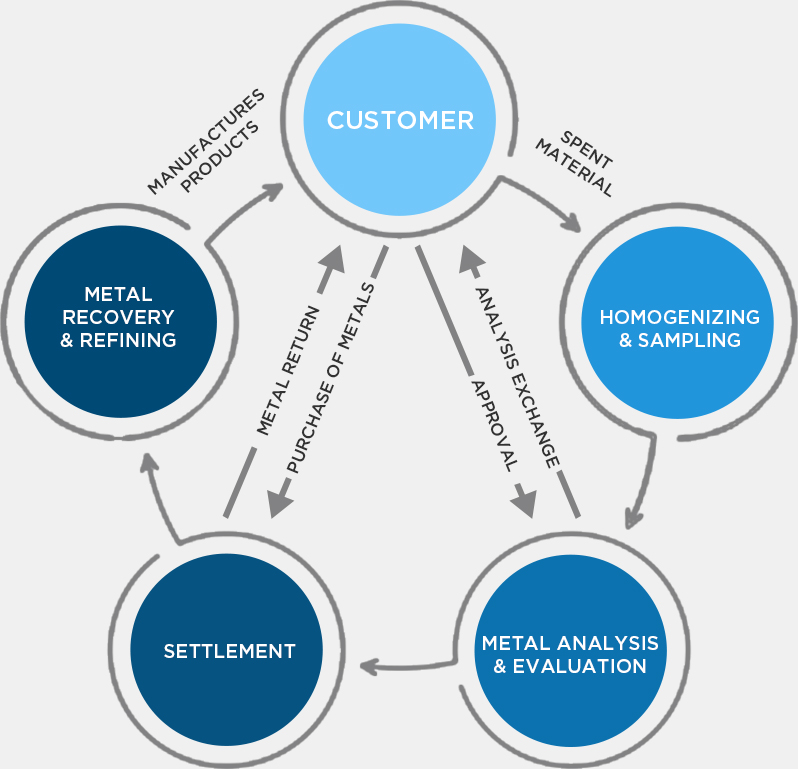
Hindustan Platinum monitors recovery of precious metals, from the time we receive used catalysts to the time we supply back recovered metals. A monthly check-up of the client’s inventory allows customers to be up to date with their stock. This also gives clients, the flexibility to use the given metal for multiple products thereby reducing stock held at their end.

Heterogeneous catalysts are extensively used in chemical industries because of their activity, selectivity and recycle capability. Industrial catalytic processes are highly cost effective as it is as it involves moderate reaction conditions, high yields, high throughputs, minimal by-products and process costs, which make the industrial process highly cost effective.
These catalysts mainly find applications in liquid phase hydrogenation, dehydrogenation, and oxidation reactions usually in stirred tank reactors. This requires finely divided material which can be easily suspended within the reaction medium.
Finely divided platinum group metal salts are supported on a high surface area material, with various loading, under extremely controlled conditions. It involves careful selection of various parameters such as a metal precursor, its concentration, pH, temperature, precipitating agent, reducing agent, sequence and rate of addition of various salts to make efficient catalysts.
The surface area of the support determines metal loading and dispersion. The pore size distribution influences the diffusion rates and controls the course of the reaction. Surface chemistry, and thermal and chemical stability of the support decides the performance of the catalyst. The metal location, its crystallite size and oxidation state influences a catalyst's selectivity. The support also facilitates improved metal recovery.
There are diverse advantages of tailored-catalyst that include strong technical assistance, capacity enhancement in short duration, higher metal return, shorter delivery time and world-class production facilities.
| SR. No. | Grade | Metal Content | Support | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RD-236 | 3%, 5% | Carbon |
|
| 2 | RD-316 | 5% | Carbon |
|
| 3 | RD-381 | 3% | Carbon |
|
| 4 | RD-451 | 1% | Carbon |
|
| 5 | RD-537 | 5% | Carbon |
|
| 6 | RD-709 | 3%, 5% | Carbon |
|
| 7 | RD-714 | 5% | Carbon |
|
| 8 | RD-741 | 3% | Carbon |
|
| 9 | RD-4112 | 5% | Carbon |
|
| 10 | RD-4086 | 1.50% | Carbon |
|
| SR. No. | Grade | Metal Content | Support | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RD-92 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 2 | RD-124 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 3 | RD-162 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 4 | RD-169 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 5 | RD-172 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 6 | RD-189 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 7 | RD-203 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 8 | RD-206 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 9 | RD-213 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 10 | RD-245 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 11 | RD-250 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 12 | RD-298 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 13 | RD-299 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 14 | RD-306 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 15 | RD-312 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 16 | RD-343 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 17 | RD-454 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 18 | RD-484 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 19 | RD-501 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 20 | RD-506 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 21 | RD-572 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 22 | RD-609 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 23 | RD-612 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 24 | RD-619 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 25 | RD-636 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 26 | RD-672 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 27 | RD-692 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 28 | RD-718 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 29 | RD-778 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 30 | RD-841 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 31 | RD-355 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 32 | RD-355 L | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 33 | RD-373 | 5%, 10% | Carbon |
|
| 34 | RD-4173 | 5% | Carbon |
|
| 35 | RD-4089 | 5% | Carbon |
|
| 36 | RD-4161 | 10% | Carbon |
|
| 37 | RD-4153 | 5% | Carbon |
|
| 38 | RD-4094 | 5% | Carbon |
|
| 39 | RD-4092 | 3% | Carbon |
|
| 40 | RD-4099 | 3% | Carbon |
|
| 41 | RD-4136 | 5% | Carbon |
|
| 42 | RD-4105 | 5% | Carbon |
|
| 43 | RD-4093 | 5% | Carbon |
|
| 44 | RD-4113 | 10% | Carbon |
|
| 45 | RD-4095 | 10% | Carbon |
|
| 46 | RD-4163 | 5% | Calcium carbonate |
|
| SR. No. | Grade | Metal Content | Support | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RD-8 | 5% | Aulmina |
|
| 2 | RD-199 | 5% | Carbon |
|
| SR. No. | Grade | Metal Content | Support | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RD-800 | 5% | Carbon |
|
| 2 | RD-4156 | 5% | Carbon |
|
| 3 | RD-4091 | 5% | Carbon |
|
| 4 | RD-4115 | 5% | Carbon |
|
| 5 | RD-4116 | 10% | Carbon |
|

Homogeneous catalysts are precious metal compounds/salts which are usually associated with organic ligands. These homogeneous catalysts offer a great advantage for chemical reaction in terms of mild reaction parameters with high activity, and selectivity such as chemoselectivity, regioselectivity, steroselectivity, enantioselectivity and recyclability. In contrast to a heterogeneous catalyst, a homogeneous catalyst and reactant are in the same phase during the entire duration of reaction, thus eliminating pore diffusion limitation on an industrial scale. As the homogeneous catalyst mechanism is better understood, manipulation of process parameter becomes easier. PGM metal homogeneous catalysts are crucial in homogeneous catalyst reactions.
The drawback of a homogeneous catalyst is difficulty in separation and recovery of catalyst. A small loss of homogeneous catalyst leads to a huge financial burden, elongated chemical process and contamination of environment making it an uneconomic process. Hindustan Platinum leads the way by providing a complete loop for recovery of PGM from spent homogeneous catalysts.
| Compound | Name | CAS | F.W. | % P.M | Solubility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (NH4)2PtCl6 |
Ammonium hexachloroplatinate(IV)
|
16919-58-7 | 443.89 | 43.95 | slightly soluble in water |
| (NH4)2PtCl4 |
Ammonium tetrachloroplatinate (II)
|
13820-41-2 | 372.98 | 52.29 | water |
| PtCl2(NH3)2 | cis-Diamminedichloroplatinum (II) | 15663-27-1 | 300.06 | 65 | in DMF |
| PtCl4(NH3)2 | trans-Diamminetetrachloroplatinum (IV) | 16893-06-4 | 370.96 | 52.6 | |
| Pt[(C2H5)2S]2Cl2 | cis-Dichlorobis (diethylsulfied) platinum (II) | 15442-57-6 | 446.37 | 43.7 | acetone, alcohol |
| PtCl2(H2NCH2NH2) |
Dichloro(ethylenediammine) platinum (II)
|
14096-51-6 | 326.1 | 59.8 | |
| H2PtCl6.6H2O |
Dihydrogen hexachloroplatinate (IV)
|
26023-84-7 |
409.82
|
water, acetone,alcohol | |
| (CH3)3Ptl | Iodotrimethylplatinum (IV) | 14364-93-3 | 367.09 | 53.1 | |
| Pt | Platinum black | 07440-06-4 | 195.08 | 98 | |
| PtCl2 | Platinum chloride (II) | 10025-65-7 | 266 | 73 | HCl, NH4OH |
| PtCl4 |
Platinum chloride (IV)
|
13454-96-1 | 336.9 | 57.9 | H2O, HCl, acetone |
| PtO2.xH2O | Platinum (IV) oxide | 1314-15-4 |
227.09
|
80-84 | |
| Pt | Platinum sponge | 07440-06-4 | 195.08 | 99.95+ | aquaregia |
| K2PtCl4 |
Potassium tetrachloroplatinate
|
10025-99-7 | 415.11 | 46.99 | water |
| Na2PtCl6.6H2O |
Sodium hexachloroplatinate (IV)
|
19583-77-8 |
453.79
|
34 | water, acetone, alcohol |
| Pt(NH3)4Cl2.H2O | Tetraammineplatinate (II) chloride | 1393-32-9 |
334.11
|
55.4 | water |
| Compound | Name | CAS | F.W. | % P.M | Solubility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd(NH3)2Cl2 | Trans-Dichlorodiammine palladium (II) chloride | 14323-43-4 | 211.37 | 50.3 | NH4OH |
| (NH3)2Pd(NO2)2 | Diamminepalladium (II) nitrite | 14852-83-6 | 232.47 | 46 | |
| Pd | Palladium black | 07440-05-3 | 106.4 | 98 | |
| Pd | Palladium sponge | 07440-05-3 | 106.4 | 99.95+ | |
| PdCl2 |
Palladium (II) chloride
|
7647-10-1 | 177.31 | 60 | dil. HCl |
| K2PdCl6 |
Potassium hexachloropalladate (IV)
|
16919-73-6 | 397.32 | 26.8 | slightly soluable in HCl |
| Pd(NO3)2.xH2O | Palladium (II) nitrate | 10102-05-3 | 230.43
|
46.18 | ddl,HNO3 |
| PdO | Palladium (II) oxide | 1314-08-5 | 122.4 | 87 | 48% HBr |
| K2PdCl4 |
Potassium tetrachloropalladate (II)
|
10025-98-6 | 326.42 | 32.59 | water |
| K2[Pd(CN)4].3H2O | Potassium tetracyanopalladate (II) | 14516-46-2 | 288.68
|
31.1 | |
| Na2PdCl4.xH2O | Sodium tetrachloropalladate (II) | 18284-36-1 | 294.2
|
36.17 | water,C2H5OH |
| Pd(NH3)4Cl2.H2O | Tetraamminepalladium (II) chloride | 13933-31-8 | 245.43
|
40.2 | |
| [Pd(NH3)4][PdCl4] | Tetraamminepalladium (II) tetrachloropalladate (II) | 13820-44-5 | 422.8 | 25.17 |
| Compound | Name | CAS | F.W. | % P.M | Solubility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (NH4)3RhCI6.xH2O |
Ammonium hexachlororhodate (III)
|
15336-18-2 | 369.74
|
27.83 | water |
| Rh6(CO)16 | Hexadecacarbonyl hexarhodium | 28407-51-4 | 1065.61 | 58 | sparingly soluable in CHCl3,CCl4,Ch2Cl2 |
| RhH[P(C6H5)3]4 |
Hydridotetrakis (triphenylphosphine) rhodium (I) |
18284-36-1 | 1153.09 | 8.9 | toluene, chloroform |
| K3RhCl6 |
Potassium hexachlororhodate (III)
|
13845-07-3 | 432.93 | 23.77 | |
| [Rh(CO2CH3)2]2 | Rhodium (II) acetate, dimer | 15956-28-2 | 441.99 | 46.57 | water |
| Rh | Rodium black | 7440-16-6 | 102.9 | 98 | |
| RhCl3.xH2O |
Rodium (III) chloride
|
20765-98-4 | 209.26
|
39 | water, alcohol, HCl |
| Rh | Rodium sponge | 7440-16-6 | 102.9 | 99.9+ | |
| Rh2(SO4)3 | Rodium (III) sulphate 10% solution | 10489-46-0 | 494 | 41.66 | |
| [Rh(C7H15COO)2]2 | Rhodium octanoate dimer | 73482-96-9 | 778.62 | 26.46 | hot alcohol, Ch2Cl2, toluene, acetic acid |
| Compound | Name | CAS | F.W. | % P.M | Solubility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K2RuCl5.XH2O | Potassium pentachlororuthenate (III) | 14404-33-2 | 356.54
|
28.3 | |
| RuCl3.xH2O |
Ruthenium (III) chloride
|
14898-67-9 | 207.43
|
38-43 | water, alcohol |
| Ru | Ruthenium black | 7440-18-8 | 101.07 | ||
| Ru | Ruthenium powder | 7440-18-8 | 101.07 | 99.9 |
| Compound | Name | CAS | F.W. | % P.M | Solubility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (NH4)3lrCl6.xH2O | Ammonium hexachloroiridate (III) | 15752-05-3 | 459.06 | 41.9 | |
| lr | Iridium black | 7439-88-5 | 192.22 | ||
| IrCl3.xH2O |
Iridium chloride hydrate
|
14996-61-3 | 298.58 | 64.4 | water, alcohol |
| IrO2 | Iridium (IV) oxide | 12030-49-8 | 224.2 | 85.7 | |
| Ir | Iridium sponge | 7439-88-5 | 192.22 | 99.9 | |
| Na3IrCl6.xH2O |
Sodium hexachloroiridate (III)
|
123334-23-6 | 473.89 | 40.6 | |
| K2IrCl6 |
Potassium hexachloroiridate (IV)
|
16920-56-2 | 483.12 | 39.8 |
| Compound | Name | CAS | F.W. | % P.M | Solubility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (NH4)AuCl4.xH2O | Ammonium tetrachloroaurate (III) | 13874-04-9 | 356.82 | 55.2 | water, alcohol |
| Au | Gold powder | 7440-57-5 | 196.97 | 99.95+ | |
| AuCl | Gold (I) chloride | 10294-29-8 | 232.42 | 84.75 | |
| AuCN | Gold (I) cyandide | 506-65-0 | 222.98 | 88.33 | |
| HAuCl4.xH2O |
Hydrogen tetrachloroaurate (III)
|
27988-77-8 | 339.79 | 50 | HNO3 |
| NaAuCl4.2H2O | Sodium tetrachloroaurate (III) | 13874-02-7 | 361.77
|
49.5 | water, alcohol, ether |
| KAuCl4 |
Potassium tetrachloroaurate (III)
|
13682-61-6 | 377.88 | 52.1 | water |
| Compound | Name | CAS | F.W. | % P.M | Solubility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgBr |
Silver bromide
|
7785-23-1 | 187.78 | 57.44 | partially soluble in NH3 |
| AgCl |
Silver (I) chloride
|
7783-90-6 | 143.32 | 75.26 | NH3, alkali cyanide |
| AgF |
Silver (I) fluoride
|
7775-41-9 | 126.87 | 85 | HF, NH3, CH3CN |
| Agl |
Silver (I) iodide
|
7783-96-2 | 234.77 | 45.95 | alkali cyanides & iodides |
| AgNo3 |
Silver (I) nitrate
|
7761-88-8 | 169.87 | 63.5 | water, alcohol |
| Ag2O | Silver (I) oxide | 20667-12-3 | 231.74 | 93 | dil.HNO3, NH3 |
| Ag | Silver powder | 7440-22-4 | 107.86 | 99.99 | dil.HNO3 |
| AgCOOCH3 | Silver acetate | 563-63-3 | 168.9 | 64.63 | dilute nitric acid |
| AgCOOCH(OH)CH3 | Silver lactate | 128-00-7 | 197.7 | 50-55 | water |
| Ag2CO3 | Silver carbonate | 534-16-7 | 275.75 | 78.23 | all acids |

Hindustan Platinum makes an array of high purity precious metal inorganic salts and solutions, which are used in diverse applications. Our extensive portfolio includes products that are used as precursors to manufacture catalysts for Automobiles, Pharmaceuticals and Fine Chemicals, starting material for Cancer Treatment, Plating of Jewellery and Electronics products, as well as Manufacturing of Mirrors and Voting Ink.
We can supply material from a few grams to hundreds of kilos as per customer specifications and with customized packaging. To meet the expectations of our clients, we collaborate with them, giving them tailored products to suit their needs. We provide our technical expertise and experience to improve our customers’ processes.
Our flexible and quick to respond aspect helps our customers to gain edge over their competition, thus enriching our partnership with them.
| Compound | Name | CAS | F.W. | % P.M | Solubility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt2[CH2=CH(CH3)2SiO | Platinum(0)1,1,3,3-divinyldisiloxane | 68478-92-2 | 5% Pt in | xylene , polysiloxanes | |
| Si(CH2)2CH-CH2]3 | OR Karsted Catalyst /solutionin xylene | Solutions | |||
| Pt[P(C6H5)3]4 | Tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) platinum (0) | 14221-02-4 | 1244.21 | 15.68 | benzene |
| Compound | Name | CAS | F.W. | % P.M | Solubility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Pd(C2H3O2)2]3 | Palladium (II) acetate | 3375-31-3 | 673.46 | 47.4 | as a monomer in pyridine, NH3, toluene |
| Pd[P(C6H5)2CH3]4 |
Tetrakis (methyldiphenylphosphine) palladium (0) |
24981-80-4 | 907.29 | 11.73 | |
| Pd[P(C6H5)3]4 | Tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) palladium (0) | 14221-01-3 | 1155.57 | 9.21 | C2H5OH, C6H6 |
| PdCl2[P(C6H5)3]2 | trans-Dichlorobis(triphenylphosphine) palladium (II) | 13965-03-2 | 701.89 | 15.16 | benzene, toluene |
| [PdCl(C3H5)]2 |
Allylpalladium(ll)chloride dimer
|
12012-95-2 | 365.85 | 58.13 | chloroform, benzene |
| Pd(COOCF3)2 | Palladium trifluoroacetate | 42196-31-6 | 332.45 | 31 | ether, acetone |
| PdCl2(C6H5CN)2 | Bis(benzonitrile)dichloropalladium | 14220-64-5 | 383.57 | 27 | chloroform |
| PdCl2(CH3CN)2 | Dichlorobis(acetonitrile)palladium(II) | 14592-56-4 | 259 | 40.4 | acetone, chloroform |
| Pd[(C6H5CH=CH)2CO]2 | Bis(dibenzylideneacetone )palladium(0) | 32005-36-0 | 575 | 18.5 | chloroform |
| Pd2[(C6H5CH=CH)2CO]3 |
Tris(dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium(0) |
51364-51-3 | 916 | 23.2 | chloroform |
| Pd2[(C6H5CH=CH)2CO]3.CHCI3 |
Tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium-
|
52522-40-4 | 1035 | 20.5 | chloroform |
| PdCl2[(C5H4P(C6H5)2)2Fe] | Dichloro-1,1'-bisdiphenylphosphinoferrocene | 72287-26-4 | 728 | 14.5 | moderate in chloroform |
| PdCl2[(C5H4P(C6H5)2) 2Fe] (CH3)2CO |
Dichloro-1,1'-bisdiphenylphosphinoferrocene palladium(ll)acetone adduct |
851232-71-8 | 789 | 13.7 | chloroform, dichloromethane |
|
PdCl2[(C5H4P(C6H5)2)2Fe] CH2CI2 |
Dichloro-1,1'-bisdiphenylphosphinoferrocene palladium(ll)dichloromethane adduct |
95464-05-4 | 816 | 13 | dichloromethane |
| PdCl2[(C6H5)2P(CH2)2P(C6H5)2] | Dichloro-1,1'-bisdiphenylphosphinoethane palladium(II) | 19978-61-1 | 575 | 18.5 | dichloromethane |
| PdCl2[(C6H5)2P(CH2)3P(C6H5)2] | Dichloro-1,1'-bisdiphenylphosphinopropane palladium(II) | 59831-02-6 | 590 | 18 | dichloromethane |
| PdCl2[(C6H5)2P(CH2)4P(C6H5)2] | Dichloro-1,1'-bisdiphenylphosphinobutane palladium(II) | 29964-62-3 | 603 | 18.5 | sparingly in DMF |
| Pd[P(t-C4H9)3]2 |
Bis-tri-t butylphosphine palladium(0)
|
53199-31-8 | 510 | 20.9 | not soluble, but decomposes |
|
PdCl(CH |
Benzyl(chloro)Bis triphenylphosphine palladium(II) | 22784-59-4 | 757.58 | 14 | dichloromethane |
| PdCl2[(C4H9)2P(C5H4)]2Fe | 1,1-Bis(di-tert butylphosphineo)ferrocene palladium(ll)chloride | 95408-45-0 | 651 | 16.3 | not soluble |
| PdCl2(C7H8) | Dichloro(norbornadiene)palladium(II) | 12317-46-3 | 269 | 39.5 | chloroform |
| PdCl2(C8H12) | Dichloro(1,5-cyclooctadiene)palladium(II) | 12107-56-1 | 286 | 37.3 | moderate in dichloromethane |
| Compound | Name | CAS | F.W. | % P.M | Solubility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [RhCl(C8H12)]2 | Chloro(1,5-cyclooctadiene)rhodium(l)dimer | 12092-47-6 | 493 | 41.7 | acetone, methanol |
| RhCl(CO)[P(C6H5)3]2 | Carbonylchlorobis (triphenylphosphine)rhodium (I) | 13938-94-8 | 690.71 | 15 | acetone, ethanol |
| [RhCl(C2H4)2]2 |
Chlorobis (ethylene) rhodium (I) dimer
|
12081-16-2 | 388.93 | 52.9 | |
| [Rh(C8H12)Cl]2 |
Chloro(1,5-cyclooctadiene)rhodium(I) dimer
|
12092-47-6 | 493.08 | 41 | sparingly soluble in common solvents |
| RhCl[(C6H5)3P]3 | Chlorotris (triphenylphosphine) rhodium (I) | 14694-95-2 | 925.23 | 11.1 | benzene, toluene |
| RhCl2(C2H8N2)2NO3 | trans-Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine) rhodium(lll)nitrate | 356.01 | 28.9 | ||
| RhH[P(C6H5)3]4 |
Hydridotetrakis (triphenylphosphine) rhodium (I) |
18284-36-1 | 1153.09 | 8 | |
| [Rh(CO2CH3)2]2 | Rhodium (II) acetate, dimer | 15956-28-2 | 441.99 | 46.57 | water |
| [Rh(C7H15COO)2]2 | Rhodium octanoate dimer | 73482-96-9 | 778.62 | 26.46 | hot alcohol, CH2Cl2, toluene, acetic acid |
| Compound | Name | CAS | F.W. | % P.M | Solubility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RuO2.x H2O | Ruthenium (IV)Oxide, Hydrated | 32740-79-7 | 187 | 52-55 | hydrochloric acid aqueous |
| [(C8H12)RuCl2]n | Dichloro(1,5-cyclooctadiene)ruthenium(IIp)olymer | 50982-12-2 | 280 | 34-36 | not soluble |
| (CH3CH2CH2)4N+RuO-4 | Tetrapropylammonium perruthenate | 114615-82-6 | 351.43 | 28.75 | |
| [RuCl2(C10H14)]2 | Dichlorobis(p-cymene))ruthenium(ll)dimer | 52462-29-0 | 612 | 33 | alcohol |
| Ru2Cl4[(S)-BINAP]2. complex |
Ruthenium -(S)- BINAP complex
|
1690 | 11 approx | ||
| Ru(CH3COCHCOCH3)3 | Tris(acetylacetonate)ruthenium(III) | 14284-93-6 | 398 | 25.4 | chloroform |

For powder precious metals catalysts, the support has an active role to play. The surface area and hydroxyl groups present of the support determines metal loading and dispersion. The pore size distribution influences the diffusion rates and controls the course of the reaction. Surface chemistry and thermal and chemical stability of the support determines the catalyst’s performance. The metal location on the support, its crystallite size and oxidation state influences the catalyst’s selectivity.
Mostly derived from natural sources, this commonly used support is subjected to physical and chemical variations. Its surface area can range up to 1200 m2/g. The carbon supported catalyst comes as dry powder or a paste with 50% water. The former is considered potentially more pyrophoric in the presence of organic solvents and needs more skillful handling. Furthermore, handling losses are minimized by using the wet catalyst. At times the catalyst can be reused like washing with water followed by solvents. Easy recovery of precious metals can be possible by carbon incineration.
This support with a surface area of up to 300 m2/g can be produced in pure state. Apart from the surface area and porosity, other performance related parameters can be adjusted to the desired catalytic process. This well characterized support has low absorption, high thermal stability than carbon and is non-combustible.
Calcium Carbonate, Barium Carbonate and Barium Sulphate are low surface area supports with low absorptive capacity which are used for specific catalyst manufacturing.
Our catalysts are tailor-made to meet our clients’ expectations and parameters. The R&D process is effective as we co-ordinate with our customers’ technical personnel to develop the right catalyst for their applications. Every day we develop different catalysts with varying precious metal loadings ranging from 1% to 20%. Our expert team also provides solutions to customers’ production related queries and problems.
Hindustan Platinum’s commitment to quality is present across the Salts and Catalysts division. We leave no stone unturned and thoroughly analyze our manufactured catalysts at every stage of production. Our ultramodern analytical laboratory is not only equipped with chemical assay systems but also equipped to measure surface area, pore size distribution, metal distribution, metal dispersion, particle size distribution and catalyst activity, thus ensuring a consistent supply of superior quality products to our customers.

The homogenized material goes through several physical and chemical processes for optimum recovery of the precious metals. These metals then undergo refining, the final purification process, which yields precious metals of purity above 99.95%, meeting international standards.
Sampling is the crux for accurate determination of precious metal content in scrap material. This material needs to be homogenized to draw samples which represent the entire lot. Depending on the nature of the material, this can be achieved by a combination of incineration, sieving, grinding, blending & melting. Multiple representative samples are then drawn for evaluation of metal content by us, by the customer & if required by a reputed international laboratory.
Different analytical methods are employed to determine the concentration of precious metals in the homogenized sample which range from ppm level to 99.99% metal content. In addition to the traditional wet-chemical and fire assay methods, Hindustan Platinum uses advanced methods such as absorption and emission spectroscopy to reveal the exact content of precious metals. The choice of analytical methods is judiciously made depending on the type of material. Apart from this, the impurity profile is also determined for any purified metals for the manufacturing of high quality finished products. Analytical reports determining precious metals content are presented to the customer for approval & final settlement.
High purity precious metals are used to manufacture a wide array of sophisticated industrial products. All our supplies are accompanied by our Certificate of Analysis (CoA). The entire cycle of precious metal recovery is conducted through environment friendly processes which deliver high-yield, high-purity final products within the committed time.
Precious metal catalysts hold a unique position because of their high catalytic performance (activity, selectivity, filterability and recyclability). Hindustan Platinum has perfected the art and science of manufacturing homogenous and heterogenous catalysts for different industrial applications. For more than four decades, Hindustan Platinum has been serving the industry and has earned itself an enviable reputation and stature in the field of precious metal catalysts. The manufacture of precious metal catalysts involves complex procedures and processes which require strict adherence to material and process quality parameters. Every ingredient used in the development of the catalyst is sourced from approved manufacturers/vendors and analysed internally for its quality.
Hindustan Platinum covers every product with its Quality Commitment. All manufactured catalysts are subjected to analysis and quality control at every stage of production. Our state-of-the-art analytical laboratory is not only equipped with chemical assay systems but also equipment to measure surface area, pore size distribution, metal distribution, metal dispersion, particle size distribution and catalyst activity thus ensuring a consistent supply of superior quality products to our customers.
Quality and reliability is what we live by. We are constantly striving for success and aim to achieve the highest quality standards for our operations. The ISO 9001 accreditation demonstrates our commitment to providing a high-quality and consistent service to our customers.


Metal Catalysts Issue 04, October - December 2019
Metal Catalysts Issue 03, July – September 2019